
2128 ACCELERATING PEDIATRICS CASE FIND AMONG PEOPLE LIVING WITH HIV (PLHIV) IN HIGH-RISK SECURITY AREAS IN NORTH-WESTERN NIGERIA USING USING GEOSPATIAL MAPPING: USAID-ACE3 PROJECT.
Author: Oyindamola Alimi1, Alozie Ananaba1, Nkata Chuku1, Pamela Gado2, Dayo Popoola1, Lan Terhemba1, Kenneth Alau1
1Health Systems Consult Limited (HSCL) - ACE3 Project, Abuja, Nigeria.
2USAID-Nigeria, Abuja, Nigeria
Conference Track:
Track 6: Transforming Health in Africa through Digital Innovation
Introduction
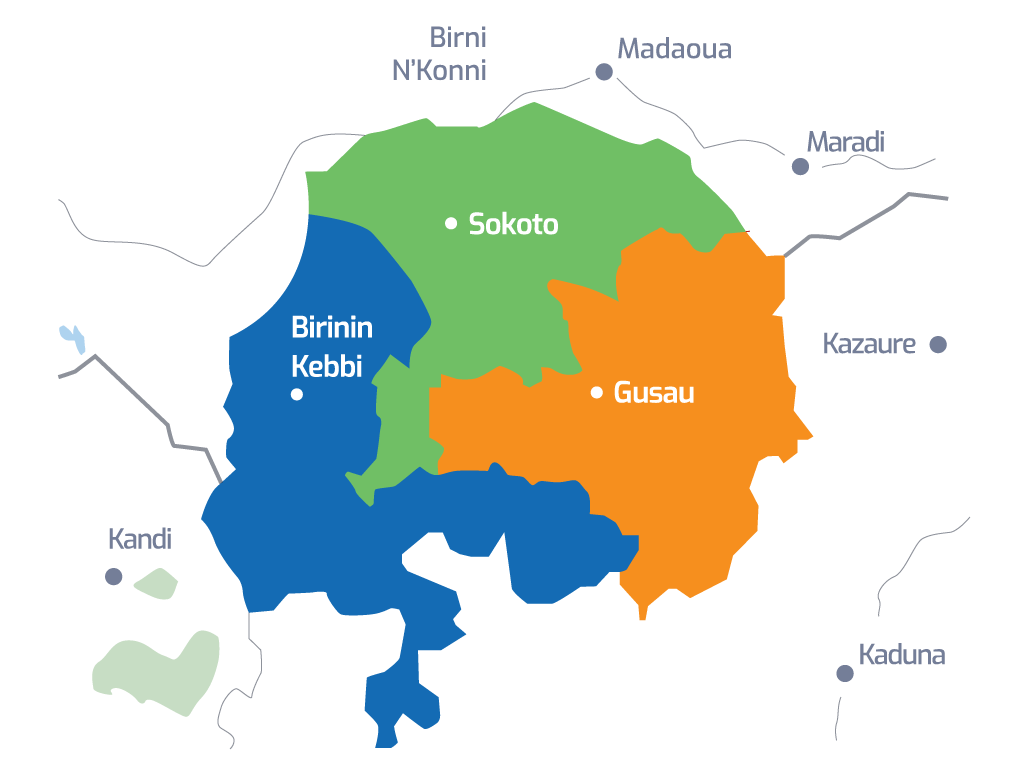
In Nigeria, pediatric HIV cases are among the underserved population across the first, second and third 95 UNAIDS global target in ending HIV/AIDS. High-risk security areas in north-western Nigeria pose significant challenges to accessing and providing comprehensive healthcare services for children living with HIV. This abstract aim to explore the effectiveness of geospatial mapping in driving pediatric case finding among people living with HIV (PLHIV) in these high-risk security areas of Kebbi, Sokoto and Zamfara.
Methods
Implementation science was designed using geospatial information systems (GIS) to identify high-risk security areas with limited access to pediatric HIV services. Demographic and epidemiological data, such as the number and age distribution of people living with HIV were collected and integrated into the GIS database. This facilitated the identification of areas with a high concentration of PLHIV, particularly children (0-14 years), and inform areas for targeted HIV case finding.
Results
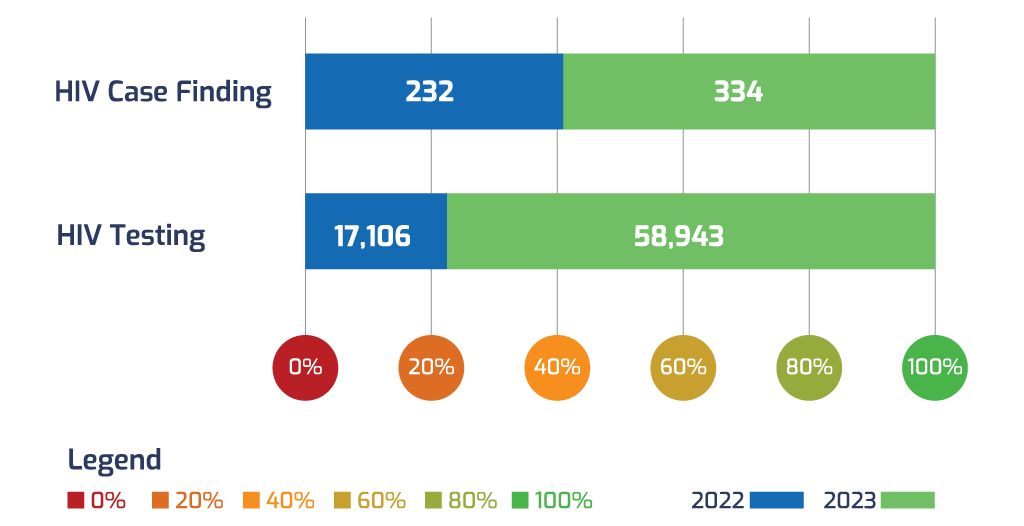
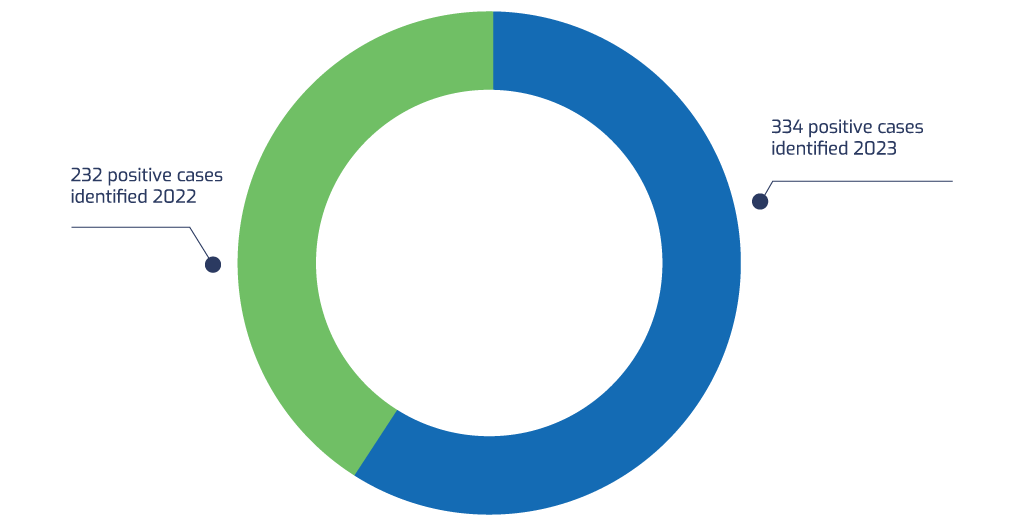
HIV testing among children within 0-14 years of age increased from 17,106 in 2022 to 58,943 in 2023 which is 345% level of increased. Similarly, HIV case finding jumped from 232 in 2022 to 334 in 2023 (44% level of increased). The 334 HIV positive children identified were successfully linked to care and treatment. Genealogy testing and family testing were also conducted among the newly identified HIV positive children which further increased the case finding.
Conclusion
Geospatial mapping techniques offer promising avenues for effective and efficient pediatric HIV case finding in high-risk security areas. The findings from this study will contribute to targeted interventions and improved health outcomes among children living with HIV in north-western Nigeria, ultimately advancing the goals of the USAID- ACE3 Project in combating pediatric HIV and enhancing overall public health in the region.
Keywords: Geospatial Mapping, PLHIV, Pediatrics, USAID-ACE3 Project

